Solar now being the cheapest energy source made its rounds on Lemmy some weeks ago, if I remember correctly. I just found this graphic and felt it was worth sharing independently.
Imagine how steep that line would be if the fossil fuel lobbies hadn’t been fighting it tooth and nail all these years
much more important: we’d be years ahead with storage technology.
I could be wrong but I don’t think there’s any evidence that the fossil fuel industry worked to suppress storage research/funding. Pretty much every IT industry has a huge interest in improving battery tech and energy storage in general, it’s just that we’ve already hit all the low hanging fruit from a chemistry standpoint
I remember hearing stories about oil companies buying up battery patents. But this may be because they want to collect the royalties, not necessarily to suppress any kind of research. But like you said, I don’t think there is any evidence… But if they were suppressing the technology, we probably would never know about it.
My dad was a VP at an oil major and has a literal story of an LNG tech being bought and shelved. Yet he’s still just like the people he complains about in that story. They’re a strange generation, these boomers.
Gotta keep prices high yo
It would be less steep because solar costs would have come down earlier.
That would make it steeper, no?
This part of the graph (2009-2019) would be less steep, because this sharp drop would have happened earlier - we’d be further along the curve
Without saying anything about politics, environment, or source:
Why, for the love of Satan, does this graph have only 2 data points per source?
Why use a line chart 📉 for that?
This is clear bar chart territory 📊.
I know it’s not ideal, but a bar chart design could either focus on the difference over time for each source, or the difference between sources at each time. This plot gives a good representation of both the differences between sources and the change in time for each source. It really drives home how far solar prices have fallen relative to other sources and in absolute terms.
It’s called a slope chart and it has several benefits compared to bar charts:
- https://datavizproject.com/data-type/slope-chart/
- https://seeingdata.org/taketime/inside-the-chart-slope-graph/
- https://www.storytellingwithdata.com/blog/2020/7/27/what-is-a-slopegraph
I for one think this is much better than using a bar chart for this use case, as the angled arrows make it immediately obvious the information that matters the most here (the rate of change) while still keeping it contextualized (by relative positions). The bar chart version of this would inevitably look more cluttered and would not be more effective in conveying the incredible progress in solar costs.
The cost of the panels themselves doesn’t seem to have gone down nearly that much.
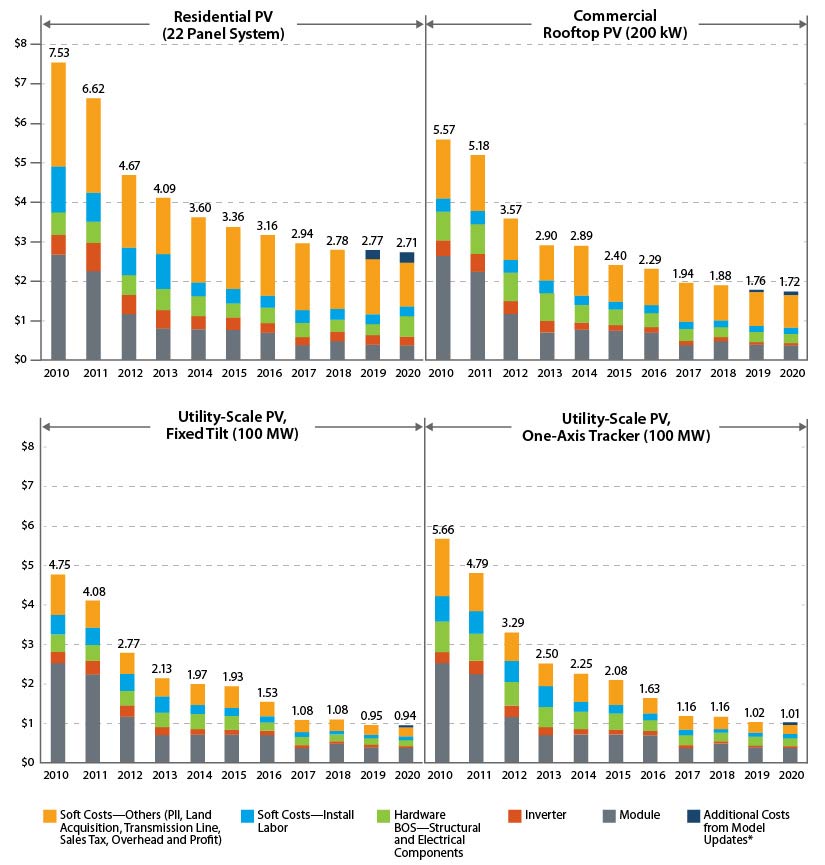
OP’s data is LCOE, which takes into account much more than $/MW. Rather importantly, expected operating liftetime is a major component (and historically THE major economic downside of PV).
IIRC, LCOE is calculated for utility-scale solar, which has seen a 500% decrease according to your chart.
Finally, Neither chart specifies, but if OP’s is in constant dollars and yours isn’t that would explain a lot as well.
What surprises me, in a way, is that photovoltaics are literally 3,5 times cheaper than just mirrors reflecting light onto a tower. It got REAL cheap. Wish it’d go further!
The mirrors are the not the expensive part.
What is? Thermal to electricity conversion?
Yup. Steam turbine generators have a lot of moving parts, and moving parts break
Got it, thanks
The installation just keeps getting higher. Now to add onto mine I need a load of additional equipment that was not required when my first lot of enphase inverters was installed. Also what was quoted for the labour and materials that are not the panels and inverters has almost tripled in 4 years. Have to get the roof sorted before I go ahead with it and the higher output panels and inverters mean that I would get about another 1.5kw in the same space compared to my first installation.
Rooftop solar is the most expensive way to do it. The graph above is for utility scale systems. Roofs are always custom jobs and they’re priced accordingly. Utility scale uses racks that are all the same for an entire field.
If rooftop was priced alone on the chart in OP, it’s be around the price of nuclear.
To ballpark some numbers on the contractor side, I charge about $100/hr to install it now - 4 years ago that might have been $60/hr.
Really depends on where you are, sadly.
Where I am, a normal 6.6kw system (panels + inverter + installation) can cost as low as about $1,950usd nothing more to pay. Good for 25 years. (Higher end panels and such can go up to about $4500usd for a 6.6-7kw system)
Damn it’s like 9k to 10k cad where I live.
Yikes, yeah, that sounds sadly normal for a lot of places.
Sweet, now get the panels and installation cheaper so I can afford to put it on my house
Further lowering panel cost isn’t going to significantly cut that price. Cost of labor is the major part of that.
People always focus on rooftop solar, but it’s horribly expensive compared to a field of panels. The economics of scale will almost certainly keep it that way.
What we should be looking at is community solar, where neighborhoods invest in a solar field together.
Wouldn’t that be a less sustainable use of land?
I guess maybe not if we are talking tall building, where the roof surface area may not be sufficient for the entire building. But it would be a waste not to make use of all the unused rooftops
Yeah, in some countries, land is at a premium. No way would it be wasted on just solar panels. Rooftop installations make the most sense.
They are even testing putting them afloat on dam reservoirs.
I’ve always thought that in the neighborhoods where everyone lives in townhomes and mini apartments a shared multi floor parkade with solar and maybe also wind on top should be a thing. Even if the solar is just covering the parkade’s power usage.
Dang, it’s almost like it was worth all the research money the government crammed into it in the long run, unlike what my dad said to me a million times.
Pretty clearly shows why there’s no future for nuclear power.
Even for filling gaps in renewables, peaker plants are getting cheaper and don’t take 15 years to build.
This is always a weird take to me because it always ignores the fact that nuclear has been screwed continuously for decades. If any other tecbology, renewable energy or not, had the same public and private blockers did it would also have no future.
it always ignores the fact that nuclear has been screwed continuously for decades
On the contrary: I’d say it implicitly relies on that fact, which is why the argument that it takes 15 years to build is valid. Because nuclear has been screwed, there’s no pipeline of under-construction plants coming online any sooner than that.
It may not be fair that nuclear’s been screwed, but that doesn’t change history. The only thing that matters is what’s better when construction is starting in 2023.
While I don’t think it relies on that fact, you are correct with the rest.
This.
Nuclear has been screwed by its own track record.
Why do you think its had such a wide coalition of public and private opponents?
Well that’s simply false. Its been screwed by ignorance propaganda and fear mongering.
You clearly don’t understand the other side.
Sure buddy. And you clearly do.
Actually I do. I was a nuclear booster in the 1990’s because it means cheap limitless pollution free power.
Except that they don’t actually deliver on that promise. You can have safe nuclear or cheap nuclear, but if it’s safe it’s not cheap, and the public rightfully won’t accept something that can require evacuating hundreds of square miles for decades.
So wise one, where are those cheap safe nuclear power plants we keep hearing about since 1950?
In France. They standardized the designs so each one isn’t a one-off and they trained more people to work in the field.
So the user above me actually gave the the answer so kudos to them but to further answer your question, there are no actually cheap reactors because the fight to actually build one is so insanely expensive. Where I live they’d been trying to build a reactor for over a decade. Constant lawsuits and legal battles after already obtaining permits and everything. Its ballooned the cost by tenfold. Why? Because of constant NGO pressure from the likes of greenpeace. So congrats, you win. They aren’t cheap cause of the hell we’ve made for ourselves.
the other side is big oil
LOL. It’s “big solar” that’s eating their lunch.
yeah but I want the power to work between 4 pm and 8 am
“Today there are about 440 nuclear power reactors operating in 32 countries plus Taiwan, with a combined capacity of about 390 GWe. In 2022 these provided 2545 TWh, about 10% of the world’s electricity.”
There have been two major reactor accidents in the history of civil nuclear power – Chernobyl and Fukushima Daiichi. Chernobyl involved an intense fire without provision for containment, and Fukushima Daiichi severely tested the containment, allowing some release of radioactivity.
Yes- a track record of one plant failing due to Soviet incompetence and political blunders; and the second failing due to checks notes a 9.0 magnitude almost direct earthquake and ensuing 133 ft tsunami.
Worth noting that the Fukushima disaster would have been prevented if they heeded warnings in a 2008 report that said their sea walls were too short, so again incompetence.
the earthquake didn’t even damage the plant, they thought of that. the tsunami knocked out the power lines and bad generator placement led to loss of power for cooling. build reactors to passively cool themselves (which should just be a mandatory safety feature on new reactors tbh, it’s not a big ask and improves safety a lot) and fukushima type accidents become impossible. that plant was so old that the original operating license was going to expire a week after the quake and the only guy who died had a heart attack. fukushima-sized death tolls happen in the rooftop solar installation industry every year, totally unreported.
Has there been a scenario where the technology itself is to blame? The contamination aspect of nuclear waste is well known and preventable, if costs are being cut on radioactive waste disposal (or in the case of a certain Japanese power company, ignoring warnings from the government on how to reduce ocean contamination in the event of an earthquake) a nuclear installation’s fate is sealed…
As far as I can see, the only downsides with nuclear IMO is that it takes multiple decades to decommission a single plant, the environmental impact on that plant’s land in the interim, and the initial cost to build the plant.
In comparison to Solar it sounds awful, but before solar, nuclear honestly would have made a lot of sense. I think it may even still be worth it in places that have a high demand for constant power generation, since Solar only generates while the sun’s about, and then you’re looking at overnight energy storage with lithium-based batteries, which have their own environmental and humanitarian challenges
Uranium powered fission technology, not all nuclear. Look into Thorium
yeah you can do throium, and there are some compelling reasons to, but uranium is fine enough. anti-nuke isn’t about actual technical enlargements. the anti nukes hate nuclear fusion too
“I’ve ignored and circumvented every known safety measure, and everything went wrong” - Whoever the fuck said that, 2023
Making up straw men to defeat?
We have extensively documented history supporting exactly what you’re trying to argue against
if you cite chernobyl that’s exactly what you’re saying. it’ll never happen again because no one’s that dumb
Fukushima happened in “smart” Japan because it was cheaper to put the backup generators in the basement than to build a concrete podium taller than the tsunamis that previously hit the site.
Capitalism will always choose cost over safety. Even then nuclear ends up going way over budget.
Then we shouldn’t leave energy security and the climate in the hands of capital. Energy should be nationalised.
you mean the part where it generated a shit ton of carbon free reliable power while killing fewer people per watt-hour what any other method? with outdated 60’s technology too? yeah sure sounds like a failure
And it is always a question how they calculated handling of nuclear waste.
There are options, we can use coal and natural gas for on demand power to fill the gaps in renewables, we don’t have to quit all at once. New ideas for energy storage and comming around, some of them might be useful for small towns, others for remote places.
deleted by creator
indeed. when you kill nuclear, the reality is natural gas and sometimes coal is the real replacement
there is very very very little nuclear waste.this is complete handwringing. it can be buried and forgotten.
Bigger issue is the carbon costs and pay back periods. Nuclear (unless you’ve got sources otherwise stating) is green in it’s planning phase but not as often in execution. A shit ton of concrete is used, and the plants rarely operate at the capacity they are expected to (or have in the past). Open to revision but that’s my current understanding.
They are a massive upfront carbon cost and only become carbon neutral or negative relative to fossil fuels 20+ years down the line.
Do you have data on that? A modern nuclear power plant is going to be in the 500-1000+ MW range. I have a hard time imagining that even operating at half capacity that they do not offset the carbon used for concrete within a relatively short order. But if that is in fact the case I’d love to see data saying so, so that I can correct my thinking.
nuclear waste, by definition of being radioactive, is the only wast that goes away on it’s own if you leave it sit for long enough
I was considering whether this is just a shitpost, but your other comments suggest that you’re completely serious. It does not go away. Radioactive decay causes multiple transitions between radioactive elements until it ends up as lead, which does not decay further.
Of course, it should also be said that it’s better to have no waste than waste that eventually turns into lead.
And that it’s still better to have waste than waste which also happens to be toxic.right, but when it lands at lead it’s no longer radioactive waste, which is the part everyone’s scared of. chemical waste doesn’t just go away like that.
Worth noting that solar panels are not without toxic waste. If left in landfills they risk leaching lead, cadmium and other toxic chemicals. The issue of recycling them at scale is not being seriously tackled.
I think that’s too simplistic of a view. Part of the high cost of nuclear is because of the somewhat niche use. As with everything, economies of scale makes things cheaper. Supporting one nuclear plant with specialized labor, parts, fuel, etc is much more expensive then supporting 100 plants, per Watt.
I can’t say more plants would drastically reduce costs. But it would definitely help.
Of course It is, the incompetent and ignorant people that try to hinder it’s use is the problem
Cool, so you’re either going to have to completely get rid of all the nimbys and people that don’t understand nuclear, then build a massive population of qualified workers to build them and staff them and then fund them in the hundreds of billions for at least 2 decades to build up the knowledge base required to be able to build them quickly and efficiently.
Or accept the reality that nuclear is dead in the water.
The nuclear industry is 100% responsible for the operational record of the nuclear industry.
the most dangerous part of nuclear power is not using enough
So the people who built that reactor were incompetent and ignorant?
Reading comprehension isn’t really your strong suit, eh? “The incompetent and ignorant people that try to hinder it’s use is the problem”
If you are hired to do a task and then overrun the budget by 14B$ I wouldn’t exactly call it furthering the cause. More like incompetence and/or trying to detail the project.
The source article actually talks about this and measured data suggests nuclear cost actually went up, despite more capacity being built.
This is the first time, I’ve read this anywhere. More sources/studies would be really important. And there is lots of interpretations to be had on the why, but assuming the article isn’t completely off the mark, that’s cold, hard data suggesting that your (perfectly reasonable) assumption is actually wrong, after all.
Interesting, I’ll have to look at the source article.
But as far as I’m aware the total amount of nuclear power has been decreasing in recent years. This might change with China’s future plants.
I’ve also read about small modular reactor designs gaining traction, which would help alleviate the heavy costs of one off plants we currently design and build.
Not saying the source is wrong, just saying that’s what I used to form my opinion.
china’s been building dozens of reactors, all of a common design which is the correct way https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hualong_One
bullshit regulatory costs can increase infinitely without nay change to the underlying engineering or economics. that’s 100% the cause of the price increses
Possible. But well, whether these regulations actually are bullshit or not, kind of doesn’t matter. A dumb solar panel won’t ever need to be regulated as much. If that’s what makes it cheaper, it still is cheaper.
They’ve had 75 years to get the cost down. It’s still going up.
because of oil funded fear pushing pseudoscience based restrictions
Congratulate yourself then. The propaganda you and your ilk continue to spew is the reason for this.
Oh it’s just the meanies keeping the poor nuclear industry down! 😆
big oil pushes this stuff, by the way. because they know the reality that when nuclear plants get shut down, natural gas replaces it
Is this just the cost per raw Watt produced?
Is it a fair comparison vs conventional fuel-based power (coal/nuclear)?
Ie: if you wanted to build a plant capable of producing continuously, 24 hours a day, you would need some multiple of solar panels to produce an excess during daylight, and storage.
Not that drastic drops in solar costs aren’t bad, just what would the cost-per-watt be if you had to power an average city on just solar for a year?
Look at the subtitle on the chart, it’s levelized cost over the generator’s lifetime. So not including storage for any intermittent source like solar or wind
And not including the financing cost of buying up an this upfront.
I’m buying 36kWh solar array and it will be home made diy, used.parts and maximum jank and don’t paid upfront because that’s the only way it makes economic sense and that’s hoping it works for more than 7 years (break even point at my insolation level and and grid price (8.8$cad/kWh) and it only works with net metering)
Levelized cost averages the fixed costs over the lifetime of the generation
They’re generally comparing utility scale installations, not home rooftop solar though.
In my area, you don’t get any government incentives unless it is professionally installed. They get you coming and going.
Yes, I never even considered the subsidies, I know it’s not for me.
Anybody can claim the tax credit though. When you file the taxes it’s a box you enter a number into.
They don’t ask for proof, but you’d better keep your receipts just in case.
Hmmmm, interesting. Thanks.
Well you’ll never get a “fair” comparison, because the environmental effects are never properly priced into the consumer price.
I just installed a 9.3 kW system with individual microinverters under each panel for grid stability and it is absolutely amazing how much you can power all day without threatening a massive bill at the end of the month. I still import power at night, but the power companies usually have agreements where you get credits for all wattage exported to the grid to cover your imported power at night, because both parties win in that contract.
Do you mind sharing what price one can expect for an install that size (or similar)? I’ve been wanting to install a system like that on my house for a couple years. Now that prices on hardware are more affordable it’s becoming very tempting. I’d love to do it myself.
It depends, $180/mo for 25 years is the agreement and it’s directly connected to the grid both ways which required additional work from the power company to inspect and approve. I think given the projections it was rated for about 25,000 kWh per year * 25 years (approaching 85% efficiency after 30 years), which is a good amount of total production for my needs. Edit: it’s worth considering what $180/mo will look like in 5 to 20 years… it will probably be significantly cheaper compared to other power sources because it’s generated locally.
Yes the time value of money can work heavily in your favor when projecting that far out. The way the housing market is right now, I might be here for a while 🤣 Thanks for the response!
Well, looking at these prices here listed seems like solar in US is really costly for some reason? I have a 9.8kWp system in europe, installed a year or two ago, and it cost me 12k euros. Out of that, I’ll get 2ke back in tax rebates, so 1ke for 1kwp.
During summertime, I get 1500kWh approx in a month. I have one AC unit and two electric cars, and a 24U server rack, and can live without electricity bills some months.
AUS here, I just got a 10kw system installed last month, cost 9.5k AUD for everything. So far monitoring the generation, I’ll be getting paid next time the bill comes around :)
deleted by creator
Where are you located and what was the total cost? When I last got quotes 12 years ago, it was insanely expensive ($ 70k ) .
deleted by creator
Is it free standing or rooftop? Many consumer companies didn’t do free standing when I last looked into it.
deleted by creator
I hate that PGE got rid of the export.
It’s frustrating seeing a graph showing the price of electricity going down while my utility prices go up. Does this take into account infrastructure cost?
deleted by creator
Yeah energy prices have gone through the roof but apparently it’s cheaper in every way except nuclear - and we don’t even have nuclear around here
The data stops in 2019. It’s completely outdated. The world is in chaos since covid. But anti nuke propagandists don’t care much about these “details”.
Hi, I’m a human being, not an “anti nuke propagandist”. I just checked, if there’s newer data, and well, there is, but no one seems to have formatted that in a way yet, which you or me would be willing to digest.
Personally, my impression has been that the solar industry was one of the industries that was pretty much completely unaffected by COVID, so I felt this graph was still perfectly relevant.
But even if it were strongly affected, I do not see why our technological progress in manufacturing, that we had in 2019, should evaporate with COVID.
There is inflation and a rise in natural catastrophes, but I feel like those would affect nuclear and others roughly proportional.Well, if you omit batteries then you are mostly true, although with covid there was a huge shortage of electronic components that would affect solar a lot, at least depending on where you live. Batteries is a big unknown now, because with all the demand for it, we simply can’t build enough batteries to feed all the grids with it.
Alright, yeah, good point with the batteries. I’m hoping the batteries in electric cars will double up as storage for the grid (already happening today), but also that there’s just enough redundancy with other renewables.
https://www.powerengineeringint.com/renewables/lcoe-for-offshore-wind-now-on-par-with-coal-bnef/amp/
Covid actually had almost no impact on the prices and they continued to level off a little lower. The surprising one is the onshore wind remaining on par with solar and continues to drop (albeit slowely).
Gas skyrocketed in Europe. Oil is going yo-yo. How does this have no impact on the price?
Thanks, China.
And Germany!
Government subsidies work for getting new technologies out of the prototype stage and into practical deployment. Solar and wind are both good demonstrations.
Removed by mod
As far offgrid as fiber will go!
I want a battery in my house big enough for me to lose power for 2 days and still cook with electric stove and have hot water from water heater.
That is my dream for every house. To be able to have a stable power well from some kind of battery fed by a solar + grid sharing. To be able to offer extra power to a neighbor if they need it for a project or a party or help however.
I don’t want to be energy isolated from the grid. I want to be energy insulated and be of the grid.
There is this vision for the future, where people can use the battery in their electric car (or a separately bought battery) to store power, either produced by their own cheap solar or from the grid during over-production. And then some software could sell that energy back into the grid at night or during high demand.
If that becomes a reality, we might have it at least so that if a chunk of the grid gets cut off for a bit, it can actually tide that over.
This isn’t so much a vision for the future, as it’s an option right now.
I can’t wait until work puts in car chargers- Top off the battery for free during the day, come home and sell that juice back to the grid, baby!
Hydrogen is the answer for that, cost about 100k today hopefully those cost will decline fast
The problem with Hydrogen, is that its not efficient (fuel cells apparently are only 40-60% efficient). In contrast, batteries are 90% or more efficient (and improving)
So, you’d be wasting 50% of the power generated, and wasting fresh water too… Thats all assuming too that the additional minerals in the water won’t cause extra issues either.
Battery costs keep dropping, and the technology keeps improving rapidly.
If they can get the efficiency much higher, maybe… It also might make sense for long range cars (at the moment) due to energy density
But, in practice, companies like BP and traditional gas companies are the main ones who benefit from a hydrogen economy. Because they can use non-renewable to undercut everyone
Cool…but where’s offshore wind?
I’m not quite sure, why it was left out of that graph, maybe they didn’t have matching data, but it is shown here (from the same source article):
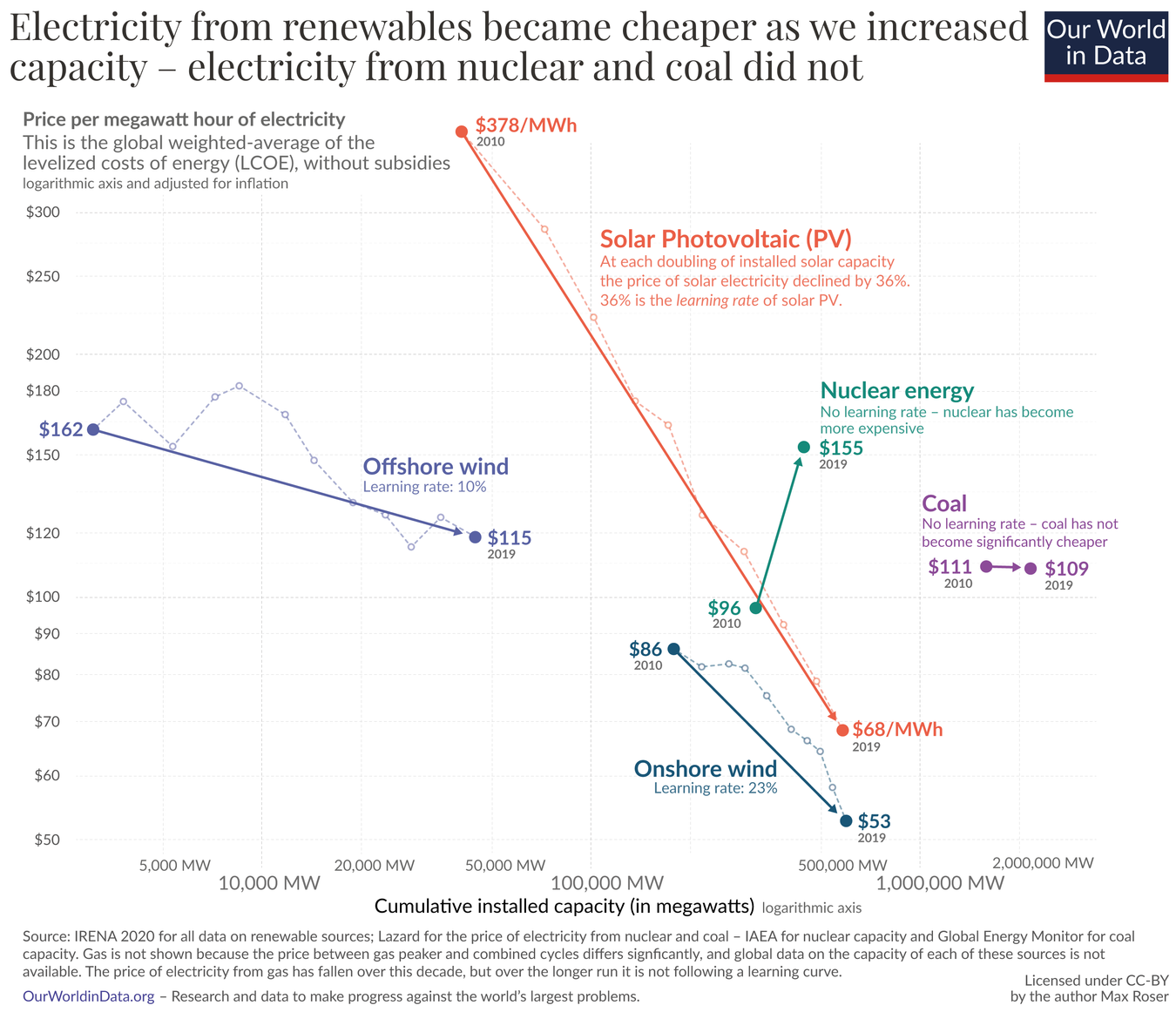
Clearly nuclear is the future!
You do realise solar and wind gets pricier and pricier to integrate as the level of steerable capacity decreases?
What you are looking at here is “cost to install ‘rated capacity * load factor’”. A big part of the reason renewables are still cheaper is that we have a lot of backup steerable capacity, mainly in the form of gas plants in the west and coal plants everywhere else.
Renewables dump electricity onto the grid and then say “here, buy this!”. And the only reason the grid can respond and say “sure” is that it can tell the steerable gas and coal plants “turn off for a bit, these other plants are dumping a crap tonne of capacity onto the grid”.
Given the insane challenge in building enough storage and/or enough transmission capacity, you are going to need some steerable capacity beyond 70-80% renewable to continue to have cheap integration of intermittent renewables. Do you want that to be based on fossil fuel?
If we wanted to treat renewable capacity in the same way as we have treated other generators, we should say “I want steerable capacity between 0-1200 MW” from this field of wind turbines!”. That would force the currently externalised cost of guaranteeing generation onto the builders of renewables.
Right now, a lot of the real cost is hidden elsewhere in the grid - so it’s no wonder it looks so cheap.
Please don’t misread my comment as being against renewables, which we need a lot more of. I’m against crappy accounting.
However, your point also goes ageinst nuclear as this technology is not really steerable either. It produces a base supply. The lack of quick control of nuclear plant output even led to highways beeing lit in the night in Belgium (way back) to burn off the over supply.
The only technologies that can be quickly adjusted up and down are, to my knowledge, gas, hydro an battery storage. In a strictly renewable scenario (0 fossil, 0 nuclear fisson) it is imperative to have a lot of controllable reserves. Currently the plan is to use a mix of (pump) hydro, h2 and biomass powered gas plants and batteries in all shapes and forms (li-Ion, reflow, heat…) to be able to compensate peaks. This all is way more costly than just using wind and solar and hope supply will always be higher than demand.
For those interested I always recommend the yt channel “just have a think”. It has really awesome content about green technologies and the current state of affairs concerning the long and hard journey to 0 carbon.
That is honestly an urban myth that nuclear isn’t steerable. It’s not steerable in the second, but it is extremely steerable in the hour or the day, which is more than plenty given that renewables output change by the hour or day, rather than the second.
Yes it’s not frequency management - for that we have pumped storage and batteries. But it sure as shit is steerable enough for matching up with renewables. The wind doesn’t goes from Beaufort 6 to Beaufort 1 within a second.
This is a very interesting rabit hole you sent me into. Thanks for that!
Btw. I don’t get why you’re beeing downvoted. This is a civilised discussion and your comments are fair and well presented!I started searching a bit about steering nuclear.
So as usual it doesn’t seem to be quite so simple. I found a paper from 2017 (in German https://publikationen.bibliothek.kit.edu/1000102277/121070976 ). interesting parts translated through deepl/chatGPT:
"The operating manuals of the NPPs show that they [nuclear power plants] exhibit considerable flexibility:
In the range close to full load (above 80/90% of the nominal Power), the output can be increased or decreased by up to 10% of the nominal output per minute. In the upper load range (above 50/60 % PNenn), the power plants can be regulated at 3.8-5.2 %/min (for some reactor types, this is reduced to around 1 %/min if individual fuel rods are defective).For comparison: In lignite-fired power plants, this value is around 3 %/min, 4 %/min for hard coal-fired power plants and 6 %/min for natural gas steam or combined power plants 6 %/min. Only gas turbines, at 12 %/min, are significantly faster.
The lower load range (between 20 and 60%) is also possible, but in discussions with power plant operators it became clear that this has not yet been used in regular operation (apart from start-up and shutdown operations) and is not used in regular operation."
Also it seems that changing output puts stress on the whole systen. As well cited from the paper:
“Another factor is the number of cycles that the plants can undergo. Each load cycle stresses the material and, with frequent repetition, leads to signs of material fatigue. Nuclear power plants were designed for a specific maximum number of cycles during their construction. In the upper load range – for example, a reduction in power from 100% rated power to 80% and back (100-80-100) – coolant temperature and pressure hardly change. Therefore, the power plants are designed for up to 100,000 cycles of such nature. However, in the lower load range, the alternating stress on the components increases, and the maximum cycle count decreases significantly. The cycle 100-40-100, for instance, is allowed only 12,000 repetitions. For the cycle rated load-zero load-hot-rated load (100-0-100), a maximum of 400 cycles is specified. Assuming a plant lifespan of 40 years, this would correspond to 10 of these events per year.”So there seems to be considerable flexibility but you don’t want to shut it off completely or run below say 50% of nominal power. Also start-up times from 0 seem to be very long (1-2 days). This might not be the perfect match for running together with renewables, but there are definitively possibilities. Even when it’s windy and the sun shines, renewables would need to be shut down and the more expensive nuclear plant would run and burn fuel.
Therefore, my opinion still stands: the ultimate goal should still be 0 burning stuff, 0 nuclear.Hey, likewise, thanks for a sensible debate.
I definitely think 0 nuclear is possible, just a lot expensive than “mostly renewable with some nuclear.”
I’ve commented extensively on this before here on Lemmy, let me copy pasta here:
Here’s a couple of good papers and articles on the topic:
A systematic review of the costs and impacts of integrating variable renewables into power grids - a large meta-study from Nature Energy showing that the externalised additional cost of integrating 1 MW of renewable production hits £40/MWh between 75% to 85% renewable penetration. Beyond that no studies have been done, but already at this level, renewable would be more expensive than nuclear (at auctioned build-prices today).
Real-World Challenges with a Rapid Transition to 100% Renewable Power Systems - finds that even if you set the Value of Lost Load to £40,000/MWh in a 100% renewable grid, you’ll still get power outages after 2030. It’s not equivalent to externalised cost of renewable integration, but is a heavy indicator that without forcing massive fines on renewable providers, the reserve capacity won’t be provided (it’ll be cheaper for them to just pay the fine). The study finds that a fine of £4 million (!) per required-but-not-fulfilled MWh is needed to encourage providers build the reserve capacity (through distribution, storage etc.).
How much can nuclear power reduce climate mitigation cost? - shows that nuclear will lower the cost of getting to zero carbon electricity product by 40%+, compared to refusing to use nuclear energy production.
Burden of proof: A comprehensive review of the feasibility of 100% renewable-electricity systems - shows some of the challenges of the assumptions that people make in thinking renewables will get us all the way there.
Projected Costs of Generating Electricity - shows that, all costs considered, nuclear remains an extremely cheap way to create energy, even up against renewables.
Local Complementarity of Wind and Solar Energy Resources over Europe: An Assessment Study from a Meteorological Perspective - shows that at least in Europe, wind and sun don’t anti-correlate (in other words, we’re not going to get energy from the sun on non-windy days and energy from the wind on cloudy days. Also shows there are many periods (days long) in Europe where we have don’t get neither sun nor wind. So storage will have to last us days across Europe.
Many of these articles refer to many other articles you may find interesting.
Overall, my point is that it does us (collective “us”, not just “you and me”) no good to argue that “it’ll be alright if we just commit to renewables”. One has to argue against these peer reviewed studies, done by experts in the field, many collecting and meta-reviewing many other studies, to argue that “renewables will be enough”.
And these are not “cooky studies” in “cooky journals”. Nature, Cell, Joule are some of the most respected journals, with the highest impact ratings and the authors & their reviewers have studied these topics for years.
I’m all for more renewables! But it won’t be enough!
also since fuel costs aren’t really a problem for nuclear power, you can just throw away excess generation. not the best idea but perfectly possible in a pinch
Wind and solar complement each other. The sun often shines when the wind isn’t blowing. We have plenty of historical weather data on how long the lulls where neither would work for a given region. That tells you how much storage you need to fill the gap. Pad that out, and you’re good.
Nuclear does nothing to help this calculation. It’s just expensive.
Not only that, but we don’t have to do this all at once. The math often works out that getting to 95% renewable is far easier than shooting for 100%, with existing fossil fuel plants making up the remainder. This is fully achievable by 2030, by which point we want to drastically reduce emissions. Then we can worry about the last 5%.
There is no such plan for nuclear. If you had all the permits signed off and dirt being shoveled right now, then you would not have a single MW of new nuclear feeding the grid by 2030. They take too long to build. Budget and schedule overruns are the norm, and it’s a wonder that anyone is investing money into them at this point.
In fact, they aren’t. The US federal government has shown a willingness to sign permits for new nuclear plants. Nobody is buying, and there’s no mystery as to why.
deleted by creator
We just have to build a transatlantic power line - It’s always sunny somewhere in the world /s
yeah, do a nuclear backup for renewables. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Integral_Molten_Salt_Reactor this reactor outputs solar salt, which can store energy efficiently for hours and allow load following
dat place called Scotland?












